With the rapid development of the Internet, more and more isolated islands of information have been connected. On this basis, the realization of the Internet of Everything is no longer an unattainable dream. Unconsciously, we have already begun to come into contact with the related technologies and even products of the Internet of Things in our lives.
Next, I will share with you some communication protocols in the IoT scenario, hoping to inspire you more.
——Liu Yang Ruijie Networks Internet System Department Industry Consulting
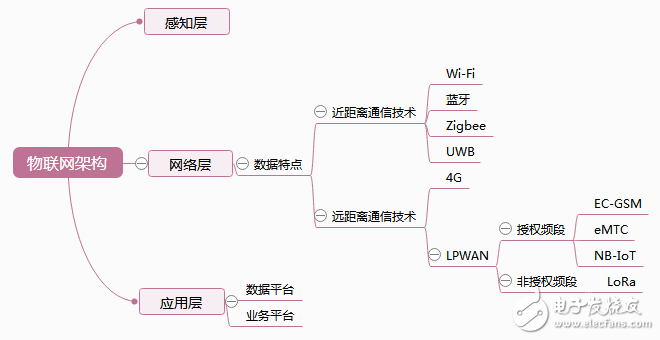
â–²Overview of the mind map of this article
The basic architecture of the Internet of Things includes three levels: perception layer, network layer and application layer.
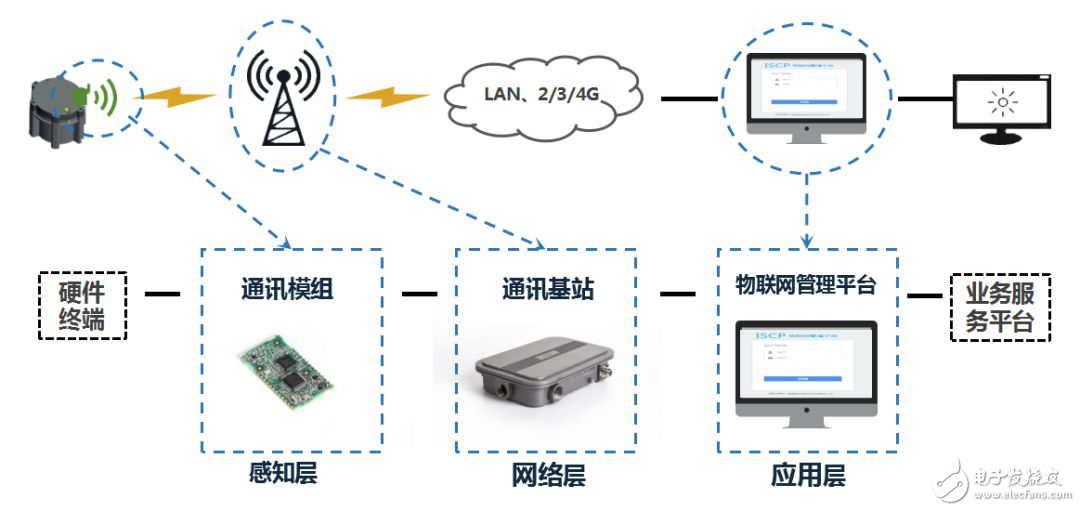
â–²Internet of things architecture diagram
The perception layer collects certain data (acoustics, light, electricity, etc.) through sensors, and terminal modules based on the network layer are connected to the base station of the network layer to realize the transmission after data collection.
The network layer is responsible for back-transmitting the data collected by the perception layer. It is important to use different communication protocol technologies for back-transmission based on different characteristics. This is also the focus of this article.
The application layer can be understood as the data platform and business platform of the Internet of Things. As the gathering point of all IoT terminal data, the data platform is responsible for the unified storage and analysis of data. Northbound provides data calls to the business platform through a standard API interface; the business platform implements various business logic based on the original data of the data platform, and external What is presented is service.
Among them, the communication protocol that focuses on the network layer is contending with a hundred schools of thought.
At present, the most popular Wi-Fi technology has fast data transmission speed, especially 802.11ax technology is about to be born. In theory, 8 streams are not a dream. However, with the increase in speed, the power consumption has increased sharply, and the transmission distance has become a problem. Long-distance transmission requires an AP to be bridged every certain distance, which will inevitably increase the cost. Therefore, Wi-Fi technology is more suitable for indoor wireless Internet surfing scenarios for terminal applications such as PCs and PDAs.
Bluetooth technology and Wi-Fi have a handover on the 2.4G frequency band, so there will be some interference problems in the same frequency band. The power consumption of Bluetooth is slightly lower than that of Wi-Fi, and the transmission speed is far lower than that of Wi-Fi. There are many applications in scenarios such as asset tracking, location tags, and medical sensors, such as smart watches and Bluetooth positioning.
The power consumption of Zigbee technology is relatively small, and the communication distance is relatively short. It is a short-distance and low-power technology, mainly used in wireless sensors and medical scenarios.
UWB ultra-wideband technology frequency band is relatively clean, there is no interference from other frequency bands, and it is more used in high-precision positioning scenarios.
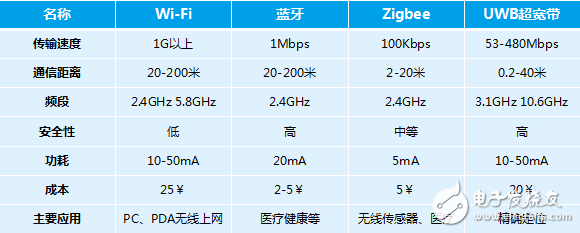
â–²Comparison of communication protocols
The above technologies are more suitable for data transmission in short-distance scenarios, so what technologies are there in long-distance scenarios?
The 4G network provided by operators is the most used in people's lives, even surpassing Wi-Fi. It can achieve long-distance transmission, regardless of indoor or outdoor, the speed is very impressive. This kind of technology seems to be superior, but its power consumption is relatively high, and it can only be applied to the Internet of Things scenarios where the terminal can obtain electricity by itself, such as a shared bicycle of a company that uses solar panels to obtain electricity.
In the long-distance scenario, if the terminal cannot solve the power supply problem, a technology with lower power consumption and larger coverage is needed to meet the IoT communication requirements in this scenario. So driven by business and technology, some experts and companies have developed a new type of communication technology-LPWAN, or low-power wide area network technology, in order to solve this problem.
The goal of LPWAN is a long-distance wireless network communication technology optimized for M2M (device-to-device) communication scenarios in IoT applications. The advantages of LPWAN technology are mainly reflected in: low speed, ultra-low power consumption, long distance, low throughput, and strong coverage. These characteristics just show that this technology is developed for the scenario of long-distance transmission of the Internet of Things. Specific applications include: urban coverage, remote meter reading, manhole cover inspection, and offshore fishing vessel inspection.
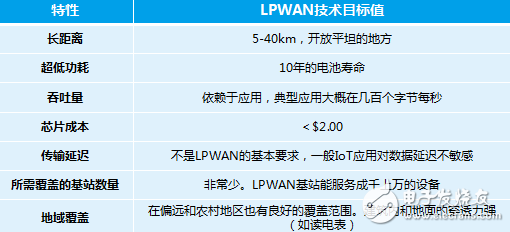
â–²Technical characteristics of LPWAN
As a new technology camp, LPWAN is divided into two major factions: authorized frequency band and unlicensed frequency band. Licensed frequency bands are divided into EC-GSM, eMTC and NB-IoT; the "top card" of unlicensed frequency bands is LoRa.
EC-GSM
With the rise of LPWAN, the disadvantages of traditional GRPS applied to the Internet of Things become more and more obvious. In 2014, the 3GPP research project proposed to migrate narrowband (200kHz) IoT technology to GSM, seeking a wider coverage range 20dB higher than traditional GPRS, and proposed five goals: improving indoor coverage performance, supporting large-scale device connections, Reduce equipment complexity, power consumption and time delay. By 2015, the TSGGERAN#67 meeting report stated that EC-GSM has met five major goals. But with the freezing of the R13NB-IoT standard, people put more energy into the redefined standard.
eMTC
The concept of eMTC is officially named in R13. The previous R12 is called Low-CostMTC, which is an Internet of Things technology based on LTE evolution. eMTC is deployed based on a cellular network, and user equipment can directly access the existing LTE network by supporting 1.4MHz radio frequency and baseband bandwidth. The key capabilities of eMTC are high speed (compared to GPRS, zigbee, etc.), mobility, location and support for voice. .
NB-IoT
NB-IoT, which is particularly hot recently, is actually the integration of NB-CIoT and NB-LTE. NB-CIoT proposes a brand-new air interface technology, which is more modified than the traditional LTE network. It satisfies the five goals proposed at the TSGGERAN#67 meeting. Its highlight is that the cost of communication modules is lower than that of GSM and NB-LTE modules. The NB-LTE is compatible with the existing LTE and is characterized by easy deployment. After fierce controversy, the two were finally merged to form the technical standard of NB-IoT.
NB-IoT is called Narrowband Internet of Things, which can be directly deployed on LTE networks, and its good compatibility reduces the cost of deployment. It has lower power consumption. In theory, the battery-based standby time of the terminal module carrying NB-IoT can be as long as 10 years. The reduction in module cost has also allowed more companies in the market to begin to apply this technology, one of which is shared bicycles that are popular across the country. The third-generation smart lock of a company uses NB-IoT modules. On the one hand, it is vigorously promoted by operators, and on the other hand, it does bring value.
LoRa
It is LoRa that develops side by side with NB-IoT. The difference is that LoRa technology uses unlicensed frequency bands. It is an ultra-long-distance wireless transmission technology based on spread spectrum technology adopted and promoted by Semtech. The full name of LoRa is LongRange. As the name implies, LoRa can support long-distance transmission. In China, there are two frequency bands that LoRa can use: CN779-787 and CN470-CN510. Since the maximum transmission power of CN779-787 is only 10dBm (10mW), it has no "practical" value. Therefore, people prefer the frequency band CN470-CN510, whose maximum transmit power can reach 17dBm (50mW).
Similar to the Wi-Fi Alliance, LoRa also has a corresponding LoRa Alliance, which aims to jointly establish standards and specifications, and LoRaWAN is such a product.
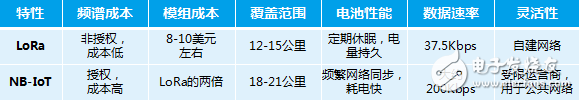
â–²Comparison between LoRa and NB-IoT
Based on cost considerations, the unit price of the LoRa module is about 8-10 US dollars, and the unlicensed frequency band does not need to pay additional spectrum costs. Compared with NB-IoT, the cost has a greater advantage. In terms of battery performance, because NB-IoT works on the cellular authorized spectrum, it needs to synchronize the network regularly, which will consume the corresponding power. LoRa has no such concerns, but this feature of NB-IoT is also warmly welcomed by shared bicycles. , Can do real-time positioning of vehicles based on this. In addition, from the perspective of the business model, NB-IoT belongs to the operator’s network construction, and the business side does not need to consider the deployment of the base station, which is more worry-free; but at the same time, the quality and security of the network are uncontrollable risks, and The value-added of the enterprise itself will also be hindered to some extent. On the other hand, LoRa is a self-built enterprise network. The base station needs to be deployed by itself, and the follow-up needs to be operated and maintained, optimized, etc., and the coverage points, network quality and security are all responsible for themselves.
Up to now, no Internet of Things technology can become the real mainstream. As far as the technology itself is concerned, there is no absolute perfection. From the perspective of business, it is necessary to combine business characteristics and business models to choose a more suitable Internet of Things technology.
The development of the Internet of Things technology is accompanied by the "heroes" from all over the world. We will wait and see if there will be a tripartite or a new power dominating the world in the future.
High Voltage STA Armored Cable
High Voltage STA Armored Cable is a type of Power Cable that is designed to carry high voltage electricity in a safe and efficient manner. It is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications where high voltage power is required for heavy machinery and equipment.
The cable is constructed with a solid or stranded copper conductor, which is insulated with a high-quality material such as XLPE or EPR. The insulation provides excellent electrical properties, such as high dielectric strength and low capacitance, which ensures that the cable can handle high voltage without any breakdown.
The cable is then wrapped with a layer of galvanized steel tape armor, which provides mechanical protection against external damage, such as impact and abrasion. The armor also helps to prevent the cable from being damaged by rodents and other animals.
Finally, the cable is covered with a sheath made of PVC or PE material, which provides additional protection against moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors. The sheath also makes the cable more resistant to fire, which is important in industrial and commercial settings.
Overall, High Voltage STA Armored Cable is a reliable and durable solution for carrying high voltage power over long distances. It is available in a range of sizes and specifications to meet the specific needs of different applications.
High Voltage STA Armored Cable,PVC Sheathed Electric Cable,Copper Conductor Power Cable,High Voltage Xlpe Power Cable
Ruitian Cable CO.,LTD. , https://www.rtlinecable.com