1 Overview Voltage transformers are important equipment components in the operation of power systems. They are the communication components between the primary system and the secondary system in the AC circuit. They are used to transmit information to supply measuring instruments, instruments and protection and control devices. It belongs to special transformers and works. The principle is basically the same as the transformer. The basic structure is mainly composed of primary winding, secondary winding and iron core. The primary and secondary windings and the iron core have matching insulation measures. Under normal conditions, the secondary circuit voltage is proportional to the primary circuit voltage.
It is not difficult to see from the principle characteristics of the voltage transformer that the secondary winding cannot be short-circuited or grounded. The magnitude of the secondary voltage, which is related to the primary voltage, the magnetic potential generated by the secondary voltage, balances the primary voltage potential. If a secondary loop short circuit fault occurs, the impedance is infinite at this time, the secondary voltage is equal to zero, and the magnetic potential is equal to zero. The primary voltage will all act on the excitation, causing the core to be severely saturated, and the sinusoidal alternating flux to become trapezoidal, twice. The winding will induce a large current, and the magnetic saturation will increase the iron loss and heat. If the duration is long, the insulation performance of the winding will be degraded or burned out. At the same time, the fuse of the secondary side fuse is blown, which affects the meter: when it is serious, it may cause the protection device to malfunction and burn the voltage transformer. To this end, the national standard DL408-91 "Electricity Safety Work Regulations" Chapter 10 "Working Requirements on Secondary Circuits of Relay Protection, Instrumentation, etc." emphasizes "strictly preventing short circuit or grounding of secondary circuit of live voltage transformer".
2 Common causes of voltage transformer secondary circuit short circuit failure reasons, there are several common reasons described below!
(1) The connection cable in the loop is short-circuited.
(2) The secondary circuit conductor is grounded by moisture, corrosion and damage, and developed into a two-phase grounding short circuit.
(3) There is a metal short-circuit defect inside, causing a short circuit in the secondary circuit.
(4) The outdoor terminal box is seriously damp and rust is generated at the terminal joint.
(5) Hidden dangers in the wiring of voltage transformers.
(6) Forgotten in the pre-test and maintenance process.
3 Regular inspection of short-circuit faults can be judged from the following phenomena through inspections, and defects are found:
(1) During the operation of the voltage transformer, the body has large uneven noise.
(2) When the voltage transformer is running, the body has a higher temperature rise and a larger odor.
(3) The meter indicator is abnormal and the protection device malfunctions.
(4) The voltage transformer burns out and the secondary winding burns out.
4 On-line monitoring and protection Because the voltage transformers have a large number of power system operations, and there are multiple sets of windings on the secondary side of each equipment, it is difficult to find fault defects in time during the inspection of the operating personnel, so that the defects exist for a long time. May eventually cause significant personal and equipment accidents. The following describes a method,
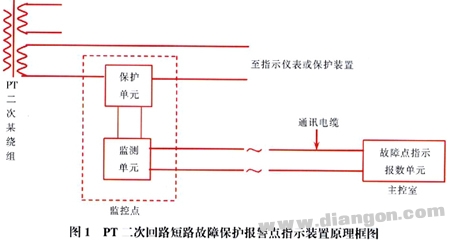
The working principle of Figure 1: The monitoring unit separately monitors the current in the PT secondary loops. When the loop current rises to a certain value for a certain period of time [Note: protection, alarm current threshold and protection action time can be set ( Initial value: current ≥8A, 20ms)], regarded as the secondary common circuit short circuit, at this time, the protection unit signal is sent to make the protection unit operate and disconnect (the unit should be connected with impedance matching function), and send it at the same time. The fault point indicates the sound and light alarm of the alarm unit (installed in the main control room) and indicates the loop where the fault point is located, which is convenient for the maintenance personnel to find the loop where the fault is located.
It can not only perform on-line monitoring, but also has the effect of eliminating the automatic defect of the secondary common-circuit short-circuit of the voltage transformer and indicating the fault point.
5 Conclusion (1) Voltage transformer secondary circuit short circuit fault can be strengthened by patrol method, through the phenomenon of faults to find defects, can also be used online monitoring methods, timely detection of hidden troubles, timely elimination, thus avoiding the fault on the person And the safety hazards of the equipment.
(2) The method of real-time monitoring of the secondary circuit short-circuit fault of the voltage transformer is also in accordance with the provisions of the DL408-91 guidelines.
GALOCE Rotary Dynamic Torque Sensors are designed to measure torque of a rotating shaft. Thus, it is necessary to transfer power to the strain gauge bridge, as well as a means to receive the signal from the rotating torque meter or shaft. This can be accomplished using slip rings, wireless telemetry, or rotary transformers. Optionally, sensors can also embed encoder for angle or speed measurement. Torque Sensor, torque transducer or torque meter is a device for measuring and recording the torque on a rotating system, such as an engine, crankshaft, gearbox, transmission, rotor, a bicycle crank or cap torque tester. fastener testing, torque to turn, installation monitoring and torque vs. clamping force.
non-contact Torque Sensor,rotary torque sensor,Torque Power Tester for Motor Speed Measurement,Power Torsion Speed Torque Rotating Sensor Measuring Instrument
GALOCE (XI'AN) M&C TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.galoce-meas.com