The application of DLP in the projector is mainly a front projection (also called front projection) system, and the rear projection field of large screen and flat panel display belongs to different application modes. Depending on the number of DMDs, DLP projectors can be divided into three types: single-chip DLP projectors, two-chip DLP projectors, and three-chip DLP projectors. There are almost no dual-chip DLP projectors in the market. The three-chip DLP is mainly used in high-end engineering and cinema-level projectors. Our main focus is on single-chip DLP technology.

Texas Instruments DLP technical analysis
Before discussing DLP technology, let's take a brief look at the history of DLP and DMD. DLP technology was developed by Dr. Larry Hornbeck of Texas Instruments. Dr. Larry Hornbeck has been working on the principles of using reflection to control ray casting since 1977 and successfully researched DMD in 1987. The DMD chip was first used in the ticket printing machine. In 1993, the DMD-based optical system was named DLP. The earliest DMD chip was driven by analog technology, and the reflective surface was made of a flexible material, which was called "Deformable Mirror De-vice" at the time. Ten years later, Dr. Hornbeck officially replaced analog technology with digital control technology, developed a new generation of DMD devices, and changed the name to "Digital Micromirror Device." In 1993, DLP projectors began to develop. In 1996, DLP products were launched, and the domestic DLP projectors officially entered the market after 1999.
From the history of DLP, it is not difficult to see that DLP technology is very young compared to LCD liquid crystal display technology. However, the emergence of DLP technology successfully broke the monopoly of LCD LCD projectors, and in the next long period of time and 3LCD technology equally divided, each occupying half of the country.

Some projector brands using DLP technology
In the years of competition with 3LCD projectors, the biggest advantage of DLP projectors is the price/performance ratio. Secondly, the DLP projector can achieve a smaller volume and a much higher contrast ratio. Of course, in the most important color display of the projector, the DLP projector has poor color saturation, easy rainbow phenomenon and low color brightness. Although TI and major manufacturers have introduced the "extreme color" technology, replacing the SDR chipset and other changes with the DDR chipset, but from the author's actual measurement situation, the same price DLP projector picture purity and so on and 3LCD projector There is a gap, which is particularly evident in industry machines. Welcome to China Home Theater Network
As the owner of DLP technology, Texas Instruments does not produce terminal products such as projectors, but only provides manufacturers with DMD chips and video processing chips, which to some extent guarantees the fairness of competition in the DLP projector market. At present, most of the world's non-Japanese projector brands use DLP technology, and DLP projectors in Japanese brands including Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, Sharp and other brands also occupy a more important position. According to incomplete statistics, the current projector brand adopting DLP technology. Already as many as 80 or so.
To make it easier for users to understand DLP technology, Texas Instruments has also produced a DEMO video to show the imaging principle of the DLP projector ( video point ). Through the video, we can see that when the light emitted by the bulb passes through the condenser lens and the color wheel, it is decomposed into three primary colors of R, G, and B and projected onto the DMD chip. The light is then reflected by the DMD lens and projected by the projection lens. Of course, readers can also get a general understanding of DLP projectors through our disassembly.
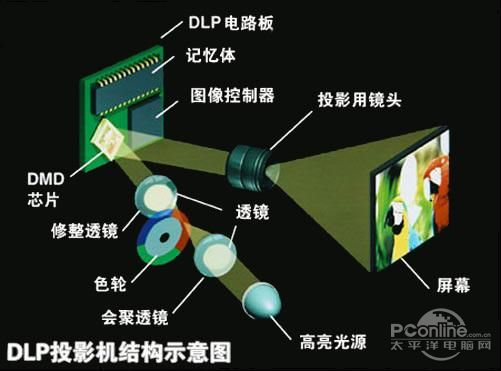
DLP projector structure diagram
If you want to explore the principle of DLP projector, you must find out the two parts of the color wheel and DMD chip. We will introduce the two parts in detail below.
COLOR WHEEL's role in DLP projectors is color separation and processing. Only single-chip DLP and two-chip DLP projectors require a color wheel, and three-chip DLP projectors do not require a color wheel. So how does the color wheel separate and process the color?
This needs to be based on the principle of light. Sunlight, incandescent light, and fluorescent light are all composite light. The light emitted by the projector bulb is of course within the scope of composite light. Composite light always contains different presentations and different frequencies of light (single-frequency light is laser). The color wheel filters the composite light into three primary colors of red, green and blue by high-speed rotation.
The surface of the color wheel is a very thin metal layer. This layer of metal is vacuum coating technology. The thickness of the coating corresponds to the spectral wavelength of the red, green and blue colors. When the white light passes through the metal coating layer, the color of the corresponding spectral wavelength will pass through the color wheel, and other colors are blocked and absorbed, thereby completing the separation and filtering of the white light.
At present, for single-chip DLP projectors, the color and brightness are inversely related. When the brightness is increased, the color will be lost, and the color will increase, and the brightness will be reduced. This is because the color of the DLP projector is RGB three colors through the color wheel. Combined, the light efficiency can only reach 60%. Of course, to improve light efficiency, you can use a colorless filter on the color wheel to achieve. When the colorless filter is added, the light efficiency can be increased by about 20%, but since the colorless filter transmits white light, it is superimposed on the three primary colors, so that the picture is brighter than its original performance, and the color is lowered. The saturation makes the color of the DLP's picture thin and produces a jitter or a flickering.
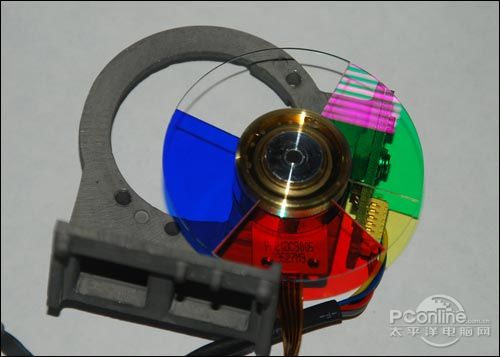
BenQ MP724 projector color wheel
Of course, the separation and filtering of the color wheel by the color wheel needs to be achieved by the high speed operation of the color wheel. It is understood that the earliest color wheel 60 revolutions per second, also known as the 1x speed. The 1x speed color wheel RGB rotates 60 times per second per color, meaning that the frequency of color appears is 60Hz. Tests have shown that when the color wheel speed is 150-250 Hz, few people can see the "rainbow effect", and when it exceeds 300 Hz, basically no one can see it.
Due to the limited speed and the working principle of the micromirror in the DMD (the working principle of the DMD we will perform the detailed second speed on the next page), the early DLP projector is prone to rainbow phenomenon. The rainbow phenomenon means that the viewer will see a red, green and blue smear on the edge of the object in the DLP projector's picture. Of course, whether you can see the rainbow phenomenon depends not only on the performance of the projector, but also on different human eyes. According to the survey, most viewers can't see the rainbow phenomenon of the DLP projector, but for the audience who can see the rainbow phenomenon. It is obviously unacceptable to say that such a poor picture performance. Welcome to China Home Theater Network
In order to solve the rainbow phenomenon, the major projector manufacturers have done a lot of work on the color wheel, the most simple and effective way is to increase the speed of the color wheel. From the early 1x speed to the current 6x speed, the current color wheel has reached a maximum speed of 360 rpm, or 360 Hz. The 6x speed wheel basically eliminates the rainbow phenomenon, but due to cost and technical limitations, most projectors currently use a 4x speed color wheel.
In addition to increasing the speed of the color wheel, DLP projector manufacturers are increasing the number of segments of the color wheel. The early color wheel consisted of three segments of red, green and blue, which not only caused rainbow phenomenon, but also the utilization rate of light was only about 60%, which is why the brightness of early DLP projectors was always below several hundred lumens. Later, Texas Instruments and DLP projector manufacturers have introduced four-stage, five-segment, six-segment, seven-segment, eight-segment color wheel... So, what are the added number of segments? What are the benefits of increasing the number of segments of the color wheel?
Among them, the four-stage color wheel adds a colorless filter to the traditional three-stage color wheel, and the light efficiency can be increased by about 20%. However, since the colorless filter transmits white light, it is superimposed on the three primary colors, making the picture brighter than its original performance. This method of adding a colorless filter (usually referred to as a white segment) increases the brightness of the projector, but the color saturation of the projector is significantly reduced. Because the transparent filter passes, it will dilute the color of the front, and will cause the illusion that the white point flashes, so it will make people feel the picture shake. This is another problem that DLP projectors have been criticized for - "color brightness" is low. Questions about color brightness can also be found here .
The five-stage color wheel adds a yellow filter to the four-stage color wheel, effectively utilizing the energy of the bulb at 580 nm. BenQ refers to this color wheel as the "golden color wheel". Toshiba will use this color. The wheel is called the "spinning wheel"... Different manufacturers have different names. The five-segment color wheel enhances the color performance of the DLP projector, but the image quality is limited and the image jitter still exists.
The six-segment color wheel is divided into several types, and the six-segment color wheel produced by different DLP projector manufacturers may be different. Among the various six-segment color wheel, the most widely used one is the double three-stage color wheel. This color wheel adopts the arrangement of red, green, blue, red, green and blue (RGBRGB) double color segments. On the basis of the color wheel, each section of the RGB filter is added. The biggest advantage of this design is to increase the frequency of RGB color. For example, the frequency of RGB color in the 1x color wheel is increased from 60Hz to 120Hz in three stages. Of course, the brightness of the projector using the 6-segment color wheel is greatly reduced due to the elimination of the white filter.
The seven-segment color wheel and the eight-segment color wheel are not discussed because of the small number of applications. Let's take a look at the other two color wheels, the SCR gain color wheel and the color wheel used in the extreme colors.
SCR (Sequential Color Recapture) is also called continuous color compensation technology. Its basic principle is similar to the above color wheel technology. The difference is that the color wheel surface adopts the Archimedes principle spiral optical coating, and the collecting column (light channel) adopts special Gain technology can compensate part of the reflected light, which greatly improves the brightness of the system (about 40%). However, the color wheel processing technology is relatively complicated, and currently only a few projector manufacturers use it in products.
BrilliantColor is a new color processing enhancement technology announced by Texas Instruments in 2005. To put it simply, the ultimate color technology is a color wheel that combines three primary colors and three complementary colors, and an appropriate color matching algorithm circuit to achieve the purpose of improving the color display capability of a single-chip DLP projector. However, it should be noted that Texas Instruments only proposed this technical concept. The DLR projector manufacturers have different color color wheel designs according to different actual conditions, so the imaging quality is also very different. However, the ultimate color technology leads DLP projectors from the traditional three-color processing to the new era of multi-color processing, destined to leave a strong stroke in the history of DLP projectors.
After spending a lot of energy on the color wheel, let's take a look at another major core of the DLP projector, the DMD chip.If the projector manufacturer can produce different products according to their actual needs in the development of the color wheel, then the DMD chip is completely in the hands of Texas Instruments. After more than ten years of development, the DMD chip has not only scaled from 0.55å‹ to 0.95å‹, but also developed from the SDR DMD chipset to the DDR chipset, and the resolution is up to 4K (the resolution of the first DMD). Only 16×16), Texas Instruments even calls the DMD chip the world's most sophisticated optical components.
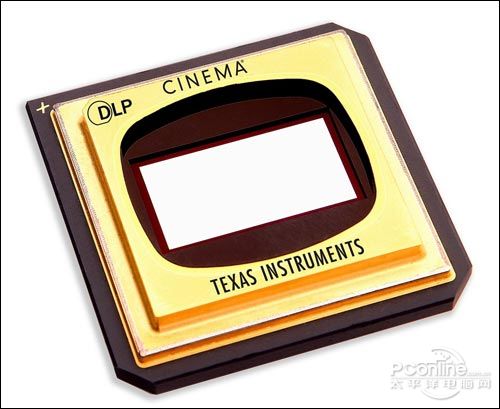

Texas Instruments Introduces 0.98-DLP Cinema DMD Chip
The role of DMD is to mix the three primary colors of light transmitted by the color wheel and convert them into color images through data control. Although it seems simple, but the technology is extremely high, how does DMD achieve this function?
DMD is an integrated MEMS superstructure circuit unit made with COMS SRAM memory cells. The DMD superstructure is fabricated from a complete CMOS memory circuit, and through the use of a photomask layer, an upper structure in which an aluminum metal layer and a hardened photoresist layer are alternately formed. The aluminum metal layer includes an address electrode, a hinge, and a hinge. A yoke and a mirror, the hardened photoresist layer acts as a sacrificial layer to form two air gaps. The aluminum metal is sputter deposited and plasma etched, and the sacrificial layer is plasma-ashed to create an air gap between the layers. Welcome to China Home Theater Network
From a technical point of view, the construction of the DMD chip includes three aspects of electronic circuit, mechanical and optical. The electronic circuit part is a control circuit, the mechanical part is a structural part for controlling the rotation of the lens, and the optical part is the lens part. When the DMD is working normally, the light passes through the DMD chip. The surface of the DMD is covered with a small volume of rotatable lenses, which will be rotated to reflect the light. The rotation of each lens is controlled by the circuit. Each mirror rotates only one color at a time (for example, a micromirror that projects a purple color pixel is only responsible for reflecting red and blue light on the projection surface, while a micromirror that projects orange-red pixels is only responsible for proportionally reflecting red and green on the projection surface. Light (high proportion of red, low proportion of green), the rotation speed of the mirror can reach thousands of revolutions, so many mirrors change at such a fast speed, after the light is projected onto the screen through the lens, the visual organ is given The illusion is that the human eye is mixed with the three primary colors of light that are flashing rapidly, so that the mixed color is seen on the projected image.
If you just want to understand how DMD works, the previous paragraph is enough. If you want to get to the bottom, let's take a look at the full and detailed understanding of the construction and workings of DMD chips.
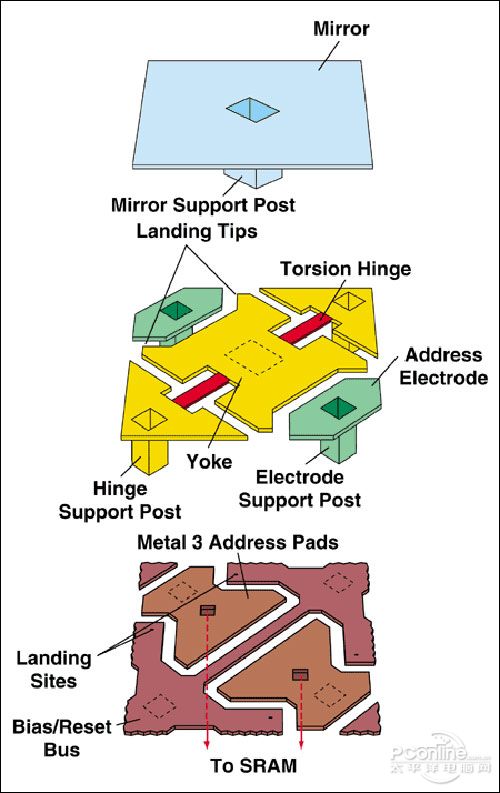
DMD chip construction
At the top of the DMD chip is composed of hundreds of thousands of microlenses with an area of ​​14×14 micrometers and smaller than the cross section of the hair. By increasing the number of microlenses in the DMD, the resolution of the product can be improved without changing the microlens. The size (for example, 786,432 small lenses on a projector DMD chip with a resolution of 1024 x 768) is linked via a device called a "yoke" below and is controlled by a "torque hinge" that can be flipped left and right. The angle of the previous lens was only 10°. Later, Texas Instruments improved and simplified the link under the lens, and the lens flip angle was increased to 12°. Although only increased by 2 degrees, the influence of stray light during imaging is greatly reduced, and the contrast index is further improved. When the memory cell is in the "ON" state, the mirror will rotate to +12 degrees. If the memory cell is in the "OFF" state, the mirror will rotate to -12 degrees. As long as the DMD is combined with the appropriate light source and projection optics, the mirror reflects the incident light into or out of the light-transmissive aperture of the projection lens, making the mirror in the "0N" state look very bright, the mirror in the "0FF" state. It looks very dark. The gray-scale effect can be obtained by using two-bit pulse width modulation. If a fixed or rotary color filter is used, and one or three DMD chips are used together, a color display effect can be obtained. A DLP projection system with a DMD chip is called a "single-chip DLP projection system", and the color filtered by the color wheel produces at least 16.7 million colors. The input of DMD is the electronic character represented by current, and the output is optical character. This optical modulation or switching technology is also called two-bit pulse width modulation, which will send 8-bit characters to each digital optical switch of DMD. At the input, 28 or 256 gray levels are produced.
At present, the optical effective area of ​​the DMD itself is greatly enhanced, and it can account for more than 90% of the surface area of ​​the entire chip, thereby effectively improving the optical utilization rate. It is also important to understand that each lens on the DMD array is electrostatically tilted to an on or off state by electronically addressing the memory cells under each lens with a binary planar signal. The technique of determining in which direction each lens is tilted is called pulse width modulation (PWM).
The "yoke" and "torque hinge" under the lens are made by a method called "surface micromachining polysilicon", which has the characteristics of stable mechanism, high flexibility and low cost. The specific implementation step is to select the aluminum alloy material for the mechanical unit and use the traditional photoresist as the sacrificial space. All work is done below 200 ° C, so adding MEMS on the wafer will not affect the metallization process or the transistor, nor will it affect the completed CMOS circuit. This method is the standard basis for MEMS micromirrors. At the same time, it solves the problem of mutual destruction of the semiconductor process, the mechanical process and the optical process. This approach is completely different from other MEMS manufacturing methods, and TI is the only company that still uses this approach.
The main working mode of the DMD chip is to control the rotation position of each micromirror on the chip according to the different signals transmitted from the back end circuit to the CMOS chip, so that the light irradiated on the micromirror has different directions of the selected reflection channels. As a miniature digital optical processing device, DMD is not only the core component of DLP projectors, but also widely used in printing, research and other fields that require digital optical switches, and has become one of the most successful products of microelectronics MEMS.
DarkChip - Many people in the projection industry are familiar with this term. We can often see that some high-end 1080p DLP projectors use the DarkChip4 chipset. So what is going on? Some projectors deliberately claim to be "data projectors" or "video projectors". DLP technology is used between them. Why is it called different?
The DLP projector with the first generation of DMD is only for business applications, the resolution is 848X600, can take into account the 800X600 SVGA computer standard and 848x480 480p (16:9) video standard. This generation of DMD micromirrors has a deflection angle of 10 degrees and a contrast ratio of 400:1 to 800:1. After that, the second-generation DMD chip launched by DLP projectors began to enter the home theater market (previous home theater projectors mostly used CRT technology), the deflection angle of the second generation chip lens was increased to 12 degrees, and the resolution was increased to 720p.
That is to say, starting from the second generation DMD chip, DLP projectors are divided into data projection (commercial) and video projection (home), which are developed according to the application direction. Texas Instruments has also made the biggest technological change to the DMD chip - the processing of the micro-mirror non-optical surface of the metal into black, which greatly reduces the stray light reflected from the metal, unprecedentedly improved the contrast of the DLP projector, this The technology is called "Darkchip 1". Of course, Darkchip is also evolving. In September 2007, Texas Instruments released the latest generation of ultra-black technology DarkChip 4, which can increase the original contrast by up to 30%.
From the current market performance, monolithic DLP projectors occupy most of the market share in the low-end market with the advantage of cost performance. In the high-end market, 3DLP technology has absolute right to speak. In the increasingly popular LED micro projectors, DLP technology is also mostly used. However, in the traditional mid-end industry market, DLP performance is not outstanding enough, there is a lot of room for improvement.
Advantages of DLP projectors
From a technical point of view, DLP projectors mainly have three characteristics: high native contrast, small machine size, and closed optical path. In the previous section, we mentioned that the DMD chip uses a mechanical working mode. The movement of the lens is more controllable, and the high contrast ratio is expected. The DLP projector adopts the reflective principle, which makes the high aperture ratio simpler. The DLP optical path system of the same configuration is smaller, and the machine can of course be smaller. In addition, the DMD chip uses a semiconductor structure, and the lens is not easy to change too much at high temperatures. Therefore, the DLP projector uses a closed optical path to reduce the probability of dust entering.
DLP projector shortcomings
The color effect of DLP projectors depends on the color wheel and DMD chip movement. The single-chip DLP projection system uses a reflective structure, especially in the low-end products. The single-chip DLP projection system is more suitable for the restoration of image color than the three primary colors. LCD projectors are a bit weaker, and the colors are not vivid enough.
Future development of DLP projection technology
According to data released by third parties recently, DLP has not surpassed 3LCD in the past 10 quarters. Although it has an advantage in the low-end and high-end markets, DLP needs to improve in the mid-market. But for DLP itself, its future is worth looking forward to. Below I will share with you the development direction of DLP in the future.
First, 3D stereo projection
According to Texas Instruments, most DLP projectors produced after 2009 can support 3D and 2D picture switching without increasing the user's input cost. Huang Zhiguang, Director of Texas Instruments DLP Asia, said that DLP will strengthen cooperation with manufacturers in the future to jointly promote the development of the 3D market. However, from the author's point of view, there are currently few 3D sources in the domestic market, and teachers using projectors rarely produce 3D courseware, so 3D stereo applications are destined to be long-term strategies. Welcome to China Home Theater Network
Second, LED micro projection application
Since the DLP optical machine can make the optical machine very small, many LED mini (handheld, pocket) projectors use DLP technology. According to data released by market research institutions, LED micro projectors have great room for development in the future, and may even become the standard for mobile phones like cameras . The number of markets has risen to the order of millions, which is not small for DLP. Good opportunity. In addition, the current LED micro projector is still in the mature stage of the market, so DLP will seize market share in the first time.
Third, strengthen the mid-market products
3D and LED micro-applications are still long-term applications. For the recent DLP projectors, it is necessary to strengthen the mid-market products. After all, this is the mainstream product in the market. Of course, this requires not only Texas Instruments to strengthen the research and development of chips, but also the strength of the mid-stream manufacturers in the promotion and promotion of the market. In particular, DLP needs to break through in the fields of industry and government procurement.
FC Optical Fiber Adapter,Sc Optical Fiber Adapter,Short Ear Sc Adapter
ShenZhen JunJin Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.jjtcl.com