Is the Chinese robot industry ready to meet the replacement of large-scale machines? Xu Xiaolan, secretary general of the World Robotics Congress, is not very sure about this. In her view, China's robot industry is still immature, independent innovation, core components are still fragile, and blindly promoting large-scale machine substitutions will inevitably lead directly to foreign countries. Importing the core components of robots and even the whole machine makes the huge Chinese market hand in hand.
In recent years, China's robot production has maintained rapid growth. Last year, sales of 90,000 units were close to one-third of the global market share. China has become the world's largest industrial robot market for four consecutive years. According to some data, by 2018, the scale of China's industrial robot market will reach 150,000 units.
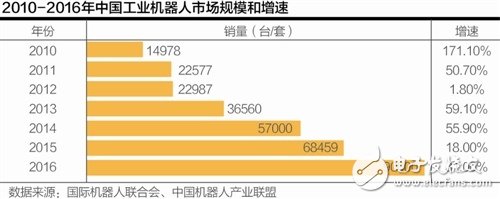
The density of robots in China is far below the world average. With the gradual disappearance of the demographic dividend and the upgrading of the industry, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta are currently pushing for machine substitutions, which has brought unprecedented opportunities for the Chinese robot industry.
However, in the face of competition with foreign brands, China's robot manufacturing industry has long been subject to core technology and parts subject to people, low-end redundant construction, enterprises "small, scattered, weak" and other issues, large-scale machine substitution for the domestic robot industry It is also not a severe test.
Pushing machine substitutions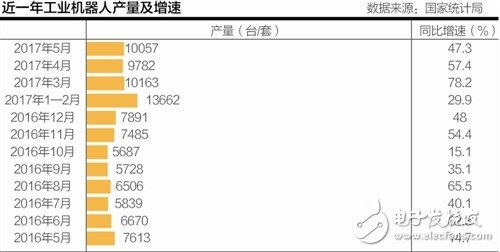
According to data released by the National Bureau of Statistics on June 14, the output of China's industrial robots in May was 10057 (sets/set), achieving a high growth rate of 47%. This is not a one-month phenomenon: the robot industry has maintained in recent years. The higher growth rate, the industrial robot production increased by 50.4% in the first five months of this year.
Looking forward, China's industrial robot market has been expanding at a very high speed in the past seven years. According to a report released by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), in 2016, China's industrial robots sold 90,000 units, a year-on-year increase of 31%, much higher than the world average of 14%.
From 2010 to 2016, China's industrial robot market has more than doubled. Since 2013, China has become the world's largest industrial robot market for four consecutive years. Its share of the global market has been from 1/5 in 2013 to It reached 1/4 in 2014 and nearly 1/3 last year.
Behind this is China's burgeoning machine substitution. Xu Xiaolan, secretary general of the World Robotics Congress, told the 21st Century Business Herald reporter that although there has not been a large-scale machine substitution phenomenon in the country, the trend has already appeared in the eastern coastal areas represented by Guangdong and Zhejiang.
She said that on the one hand, the problem of declining demographic dividends and rising labor costs in the above-mentioned areas is forcing manufacturing companies to replace people with machines; on the other hand, with the transformation and upgrading of manufacturing industries, the production methods are turning to fine and flexible, the original Manual operations may be difficult to undertake new jobs, companies may not be able to recruit the required labor, and only machine substitutions can be made.
According to Yao Zhizhen, deputy secretary general of the China Robot Industry Alliance, the layout of the robot industry coincides with the phenomenon of machine substitution. He pointed out that the current focus of machine substitution is the Pearl River Delta and the Yangtze River Delta. Among them, the Pearl River Delta is represented by Guangzhou and Foshan, and the application of industrial robots is very large; the Yangtze River Delta is represented by Shanghai and Jiangsu, and several giants of robot manufacturing are here.
In addition, he said that there are currently two regions with relatively high potential. One is the Bohai Rim region, and the industrial robots in Liaoning and Tangshan are developing rapidly; the other is the inland region represented by Chongqing.
Qu Daokui, chairman of the China Robotics Industry Alliance and president of Xinsong Robot, told the 21st Century Business Herald that the traditional advantage of Chinese companies is low-cost, labor-intensive, and the most demanding machine substitution is in industries with high technology and capital intensity. As China's industrial transformation and upgrading will be accompanied by the re-allocation of employed people.
However, Xu Xiaolan does not think that the substitution of machines will bring employment problems. She believes that the substitution of machines is the "fruit" of the demographic dividend. It is urgent to cultivate skilled workers that meet the requirements of the new era, thus promoting industrial transformation and upgrading.
Robot industry opportunities and challenges coexist
The ups and downs of the machine have brought an unprecedented opportunity for the robot industry.
According to the "Robot Industry Development Plan (2016-2020)" issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other three ministries last year, by 2020, the annual output of China's own-brand industrial robots will reach 100,000 units, and the annual output of industrial robots with six axes and above will reach 50,000. Above the station.
According to the IFR forecast, by 2018, China's industrial robot market will reach 150,000 units; by 2020, China's industrial robots will be more than 800,000 units, and the robot density (the number of industrial robots per 10,000 workers) will reach 150 or more.
From a global perspective, the average global manufacturing robot density in 2015 was 66. The density of robots in industrialized countries generally exceeded 200. However, the value of China is only 36. From this point of view, China's industrial robot market has huge space.
However, is the Chinese robot industry ready to meet the replacement of large-scale machines? Xu Xiaolan is not very sure about this. In her view, China's robot industry is still immature. Independent innovation and core components are still fragile. Blindly pushing large-scale machine substitutions will inevitably lead to the import of robot core components directly from abroad. Even the whole machine makes the huge Chinese market hand in hand.
From the structural point of view, the industrial robot is mainly composed of four parts: the body, the servo motor, the joint reducer and the controller. At present, among the three key components outside the body, the reducer and the servo motor are basically monopolized by foreign companies. The domestic robot manufacturer is subject to the control of key components. There is basically no bargaining power, and even the whole machine manufacturing cost and imported machine. Upside down, it is very passive in the market competition with foreign companies.
According to Qu Daokui's calculations, the cost of parts such as motors and reducers that Chinese robots need to import accounts for about 70% of the total cost of robots.
In application, Chinese robots are facing the dilemma of high-end market marginalization. According to Qu Daokui, at present, in the field of multi-joint robots, foreign companies account for 90% of the market, foreign brands of industrial robots with more than six axes account for 85% of the market; in the difficult welding field, foreign companies account for 84%. In the more high-end automobile manufacturing industry, foreign companies account for 90%. Domestic robot equipment applications are mainly concentrated in general industrial fields such as handling, palletizing, loading and unloading.
The other side of high-end competition is the low-end duplication of construction. The problems of “small, scattered and weak†are prominent.
According to Li Dong, Director of the Equipment Industry Department of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, there are more than 800 companies producing robots in China, of which more than 200 are robotic body manufacturing enterprises, most of which are mainly assembled and processed, at the low end of the industrial chain. Industry concentration is low and the overall scale is small. At the same time, there are more than 40 industrial parks based on the development of robots in various places, and there have been hidden concerns about low-end surplus.
Among the large number of enterprises, more than 90% of the enterprises are under 100 million yuan. Even the leading company Shenyang Xinsong, its sales revenue in 2015 is only 1.69 billion, which is related to the sales revenue of Yaskawa, FANUC and ABB. Compared with the international robot giant of 10 billion yuan, the competitiveness is insufficient.
"Compared to machine substitution, we should be more concerned about the huge domestic market potential, whether China's robot industry has the ability to independently innovate and occupy these markets." Xu Xiaolan said.
Further reading: Japanese researchers are developing a giant snake robot to explore the Fukushima Wasteland
Various universities and high-tech companies in Japan are developing various types of robots to explore the disaster area of ​​the Fukushima high-level nuclear power plant in Japan to evaluate the melting of the core area, so that future clean-up operations can be planned. The attempts by the robots they developed before attempting to reach the core location of the nuclear power plant have failed.
Despite this, robots are clearly more suitable than humans to enter and inspect this location because high levels of radiation are fatal and high levels of radiation can kill a person in a matter of minutes. The robot designed by Northeastern University is similar to a snake of up to eight meters. It can vibrate by itself, moving at a speed of 10 cm per second, and can lift the head with air pressure.
The snake-shaped robot will be equipped with a camera in the head and can be remotely controlled. The researchers hope to complete the research and development within three years. Once completed, the snake may enter the reactor to find the location of the molten nuclear fuel, and then the Japanese authorities can Begin further planning how to deal with high radioactive materials. This machine snake is also designed to search for ruins after a future earthquake, it can climb over the rubble and try to find survivors.
In addition, Toshiba has developed a bread-sized unmanned submarine that can explore the submerged portion of the destroyed nuclear power plant, which they will deploy to the Fukushima nuclear power plant this summer.
Air Gear Motor,Air Operated Gear Motor,Air Powered Gear Motor,Pneumatic Air Gear Motor
RUDONG HONGXIN MACHINERY CO.,LTD , https://www.rdhxmfr.com