The battery memory effect means that if the battery is a nickel-cadmium battery, it will not be completely charged and discharged for a long time, which will easily leave marks in the battery and reduce the battery capacity.
The meaning of the battery memory effect is that the battery seems to memorize the user's daily charging and discharging amplitude and mode. It is difficult to change this mode for a long time, and it is impossible to charge or discharge a large amount. Lithium-ion batteries do not have this effect.
Cause
Since the anode is sintered in the conventional process, the cadmium grains are coarse. If the nickel-cadmium batteries are recharged before they are completely discharged, the cadmium grains are easily aggregated to form a secondary discharge platform when the battery is discharged.
The battery stores this discharge platform and uses it as the end of the discharge in the next cycle, although the battery's own capacity allows the battery to discharge to a lower platform. The battery will only remember this low capacity during the subsequent discharge process. Also in every use, any incomplete discharge will deepen this effect, making the battery capacity even lower.
Understanding memory effect
The battery memory effect refers to the reversible failure of the battery, that is, the performance that can be restored after the battery fails. This particular tendency is automatically maintained after the battery has been subjected to a specific duty cycle for a long time. This is the earliest definition of nickel-cadmium batteries, nickel-cadmium bag batteries have no memory effect, and sintered batteries have a memory effect. This means that the battery seems to memorize the user's daily charge and discharge amplitude and mode. It is difficult to change this mode for a long time, and it is impossible to charge or discharge it. The current nickel metal hydride (commonly known as nickel hydride) battery is not subject to the definition of this memory effect, but it is inert. It must be activated a few times before. Generally, it can be charged and discharged 300-500 times. After that, it will find that the duration is coming. The shorter, the shorter you want to change your phone. Packing the old battery in the refrigerator for a few days and then using it will improve performance.
Since the anode is sintered in the conventional process, the cadmium grains are coarse. If the nickel-cadmium batteries are recharged before they are completely discharged, the cadmium grains are easily aggregated to form a secondary discharge platform when the battery is discharged. To eliminate this effect, there are two methods. One is to use a small current deep discharge (such as 0.1C to 0V), and the other is to use a large current charge and discharge (such as 1C) several times.
In practical applications, the method of eliminating memory effects has strict specifications and an operational procedure. Improper operation can be counterproductive. For nickel-cadmium batteries, the normal maintenance is regular deep discharge: a deep discharge is performed every one month (or 30 cycles) (discharge to 1.0V/per node, ie exercise). Normally, it is used as much as possible. Shutdown and other means can alleviate the formation of memory effect, but this is not exercise, because the instrument (such as mobile phone) will not use 1.0V / every section to shut down, you must have a special equipment or line to complete the work, fortunately many NiMH batteries are equipped with this feature. The battery stores this discharge platform and uses it as the end of the discharge in the next cycle, although the battery's own capacity allows the battery to discharge to a lower platform. The battery will only remember this low capacity during the subsequent discharge process. Also in every use, any incomplete discharge will deepen this effect, making the battery capacity even lower.
Lithium Ion Battery
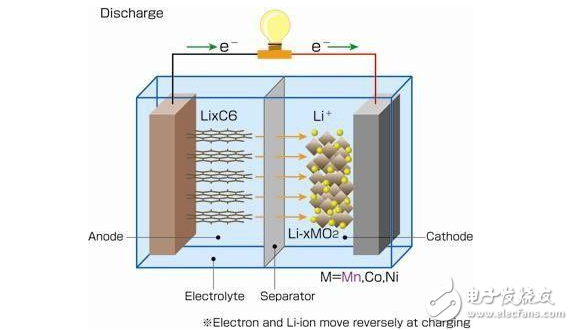
The positive electrode material of a lithium ion battery usually consists of an active compound of lithium, and the negative electrode is a carbon of a special molecular structure. The main component of the common positive electrode material is LiCoO2. When charging, the potential applied to the two poles of the battery forces the compound of the positive electrode to release lithium ions, and is embedded in the carbon in which the negative electrode molecules are arranged in a sheet structure. At the time of discharge, lithium ions are precipitated from the carbon of the sheet structure and recombined with the compound of the positive electrode. The movement of lithium ions produces electric current. Although the principle of chemical reaction is very simple, there are still many practical problems to be considered in actual industrial production: the material of the positive electrode needs additives to maintain the activity of multiple charge and discharge, and the material of the negative electrode needs to be The molecular structure level is designed to accommodate more lithium ions; the electrolyte filled between the positive and negative electrodes, in addition to being stable, also needs to have good conductivity and reduce the internal resistance of the battery.
Lithium-ion batteries generally have a management chip and a charge control chip. The management chip has a series of registers, such as capacity, temperature, ID, state of charge, number of discharges and the like. These values ​​will gradually change during use. The main function of the "use should be fully charged and discharged once a month" in the instructions for use should be to correct the improper values ​​in these registers, so that the battery's charge control and nominal capacity match the actual situation of the battery. The charging control chip mainly controls the charging process of the battery. The charging process of a lithium-ion battery is divided into two phases, a constant current fast charging phase (when the battery indicator is yellow) and a constant voltage current decreasing phase (the battery indicator flashes green).
During the constant current fast charging phase, the battery voltage is gradually increased to the standard voltage of the battery, and then transferred to the constant voltage stage under the control chip, the voltage is no longer raised to ensure that the battery is not overcharged, and the current is gradually weakened as the battery power rises. Go to zero and finish charging. The electricity statistic chip can calculate the battery's power by recording the discharge curve (voltage, current, time), which is the wh value we read in Battery InformaTIon. The lithium-ion battery will change its discharge curve after repeated use. If the chip has no chance to read the complete discharge curve again, the calculated power is not accurate. So we need to deep charge the chip to calibrate the battery.
Some controversy about lithium-ion batteries1. Does the new battery need to be activated by repeating a full charge and discharge several times?
Because lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect, the use of lithium-ion batteries does not require activation. There are indeed some rechargeable batteries that require similar "activation" work. This is the earlier nickel-cadmium rechargeable battery and nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery. These batteries produce a phenomenon called "memory effect", which is charged in an incompletely discharged state, which tends to overcharge the battery. Over time, it will cause proliferating crystals on the electrode plate and block the contact between the electrolyte and the electrode plate. As a result, the voltage of the battery drops, allowing the user to feel that the battery is quickly used up. Therefore, for both types of batteries, recharging after fully discharging the battery periodically (rather than each time) can alleviate the voltage drop caused by the above reasons. However, the batteries used in our mobile phones and laptops are mostly Li-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries, although small in size, can store large amounts of energy and are therefore used more and more widely. Lithium-ion batteries do not need to be activated by deep charge and discharge when they are used, because the battery initialization and testing process is already done when the battery is manufactured. Lithium-ion batteries also have no so-called "memory effect" and can be charged at any time. It is recommended that the lithium-ion battery be fully charged and discharged on a regular basis, just to calibrate the power detection device on laptops and some high-end smartphones, not because of the benefits of the battery itself. For ordinary mobile phones and digital cameras, the devices that display the approximate power of the battery are completely unnecessary to be fully charged and discharged periodically.
2. Does overcharging cause the battery to explode?
Lithium-ion batteries have high energy density and high voltage (the voltage generated by a single lithium-ion battery unit can reach 4.2V, while the ordinary nickel-based rechargeable battery is 1.2V). Compared with low-voltage batteries, lithium-ion batteries are charged. The redox reaction of the electrode is very severe, so the conditions of use of the lithium ion battery must be strictly limited. Overcharge, overdischarge, short circuit, high temperature, etc. can cause battery damage and even fire and explosion. However, the actual use of lithium-ion batteries is to pack a number of cells together with a set of safety protection circuits and a variety of safety devices into a battery board. These safety designs ensure that the battery's circuitry is automatically shut off during overcharging, over-discharging, and short-circuiting; excessive internal pressure in the battery can also trigger decompression of the exhaust; if the battery temperature is too high, the hot-melt protection device can be triggered to block lithium ions. The movement thus stops the electrochemical reaction of the battery. Therefore, as long as the quality of the cottage battery is not reliable, the phone is fully charged and the power is not removed in time to cause the battery to explode.
3. Can you shorten the battery life by extending the number of times you charge?
Generally, the life of a lithium ion battery can reach several hundred charge and discharge cycles, and such expressions are often seen in the specifications of batteries and equipment. Here, one charge and discharge cycle refers to the process of using the battery power and then refilling it, instead of plugging in the charger and then unplugging it once. Continuous deep charge and discharge of lithium-ion batteries has an impact on the life of lithium-ion batteries. The above hundreds of data are also measured under such conditions, but under daily shallow charge and discharge conditions, lithium-ion batteries The life span is actually quite long. In addition, lithium-ion batteries are not used, and their capacity is naturally lost. The main influencing factors are voltage and temperature. Studies have shown that lithium ions are stored for a long time in a fully charged state, and their capacity is significantly lost. Similarly, the higher the temperature, the faster the capacity loss of the lithium-ion battery, and the loss is irreversible, that is, the capacity of the battery will be permanently reduced. In a 0 degree environment, the remaining 40% of the lithium-ion battery will lose 2% of its capacity after one year of storage. In a 40 degree environment, the fully charged lithium-ion battery will lose up to 35 years after storage. %. 4. Proper use of lithium ion batteries
1. Charge the new battery:
In the use of lithium batteries, it should be noted that after the battery is placed for a period of time, it enters a sleep state. At this time, the capacity is lower than the normal value, and the use time is also shortened. However, the lithium battery is easy to activate, as long as the battery is activated after 3 to 5 normal charge and discharge cycles, and the normal capacity is restored. Due to the characteristics of the lithium battery itself, it is determined that it has almost no memory effect. Therefore, the user's new lithium battery does not require special methods and equipment during the activation process. It is best to use a standard method of charging this "natural activation" method from the beginning. The lithium battery or charger will automatically stop charging when the battery is fully charged. There is no so-called “turbulent†charging that the nickel battery charger has for 10 hours. In other words, if your lithium battery is full, it will be white charger on the charger.
None of us can guarantee that the characteristics of the battery's charge and discharge protection circuit will never change and the quality will be foolproof, so the battery will be on the edge of danger for a long time. This is another reason why we oppose long charging. In addition, on some machines, after charging for more than a certain period of time, if you do not remove the charger, then the system will not stop charging, and will start the discharge-charge cycle. Perhaps the manufacturer of this approach has its own purpose, but it is obviously unfavorable for the life of the battery. At the same time, long charging takes a long time and often needs to be carried out at night. In the case of China's power grid, the voltage at night is high in many places and fluctuates greatly. As mentioned earlier, lithium batteries are very delicate, and they are much less resistant to fluctuations in charge and discharge than nickel, which in turn poses additional risks.
2. When should I start charging during normal use:
Since the number of charge and discharge cycles is limited, the power of the lithium battery should be recharged as much as possible. For the experimental table of charge and discharge cycles for lithium-ion batteries, the data on cycle life are listed as follows: Cycle life (10% DOD): "1000 cycles life (100% DOD):" 200 times
Among them, DOD is the abbreviation of depth of discharge. As can be seen from the table, the number of chargeables is related to the depth of discharge, and the cycle life at 10% DOD is much longer than that of 100% DOD. Of course, if it is converted to the relative total capacity of the actual charge: 10% * 1000 = 100, 100% * 200 = 200, the latter's full charge and discharge is still better, under normal circumstances, there should be reserved according to the remaining battery power Use the principle of recharging, but if the battery is not expected to stick to the whole day on the second day, you should start charging in time. Of course, if you are willing to carry the charger to the office, it is a different matter.
And when you need to charge to cope with the expected important event that will lead to busy communication, even if there is still a lot of power in the battery, then only charge in advance, because there is no real loss of "1" charge cycle life, that is, "0.x" times, and often this x will be small. The principle that the remaining battery power is used up and refilled is not going to extremes. One of the more widely spread arguments like long charging is that "try to run out of battery power, it is best to use automatic shutdown." This practice is actually only a nickel battery, the purpose is to avoid the memory effect, unfortunately it is also circulating on the lithium battery. Some people have used the example of automatic shutdown since they have been warning that the machine's battery is too low. As a result, the machine in this example did not respond during subsequent charging and booting, and had to be sent to customer service for repair. This is actually caused by the battery being over-discharged and the voltage is too low, so that it does not have normal charging and power-on conditions.
3, the correct approach to lithium batteries
To sum up, my most important tips on the charge and discharge of lithium batteries in use are:
1. Charge according to standard time and procedures, even if it is the first three times;
2, when the machine is too low, you should start charging as soon as possible;
3. The activation of the lithium battery does not require a special method. The lithium battery will naturally activate during normal use of the machine.
Does the lead-acid battery have a memory effect?[1] The lead-acid battery of a battery car generally has no memory effect. It is generally an easy memory effect of zinc nicotinate. The battery lead battery is shown below:

[2] Definition: The electrode is mainly made of lead and its oxide, and the electrolyte is a kind of storage battery of sulfuric acid solution. English: Lead-acid battery. In the discharge state, the main component of the positive electrode is lead dioxide, and the main component of the negative electrode is lead; in the charged state, the main components of the positive and negative electrodes are lead sulfate. Divided into exhaust battery and maintenance-free lead-acid battery.
[3] The battery is mainly composed of a tubular positive plate, a negative plate, an electrolyte, a separator, a battery well, a battery cover, a pole, and a liquid injection cover. The electrode of the vented battery is composed of an oxide of lead and lead, and the electrolyte is an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. The main advantage is that the voltage is stable and the price is cheap; the disadvantage is that the specific energy is low.
Wireless Charging Coils,10W Wireless Charging Coil,Wireless Charging Coil For Cell Phone,Car Wireless Charging Coils
Shenzhen Sichuangge Magneto-electric Co. , Ltd , https://www.scginductor.com